Cardiac Arrest On Ecg - Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). There are four primary alterations in the.
There are four primary alterations in the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the.
The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). There are four primary alterations in the. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart.
arrhythmia, background, cardiac, cardiac arrest, cardiogram, cardiology
The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. There are four primary alterations.
Part 12 Cardiac Arrest in Special Situations Circulation
The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. There are four primary alterations.
Case 302020 A 54YearOld Man with Sudden Cardiac Arrest NEJM
Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. There are four primary alterations in the. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Pulseless electrical activity in.
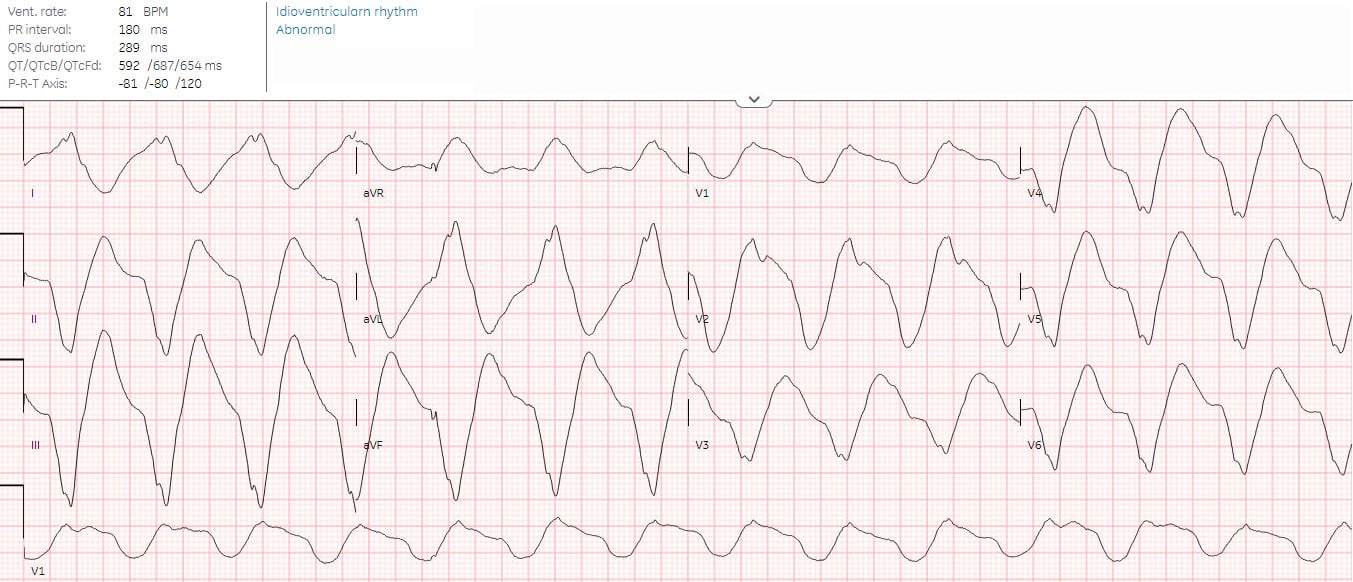
Sudden Cardiac Arrest ECG Repolarization After Resuscitation
During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: There are four primary alterations in the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and.
Case A8. Extensive Anterolateral Infarction leading to cardiac arrest
There are four primary alterations in the. Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and.
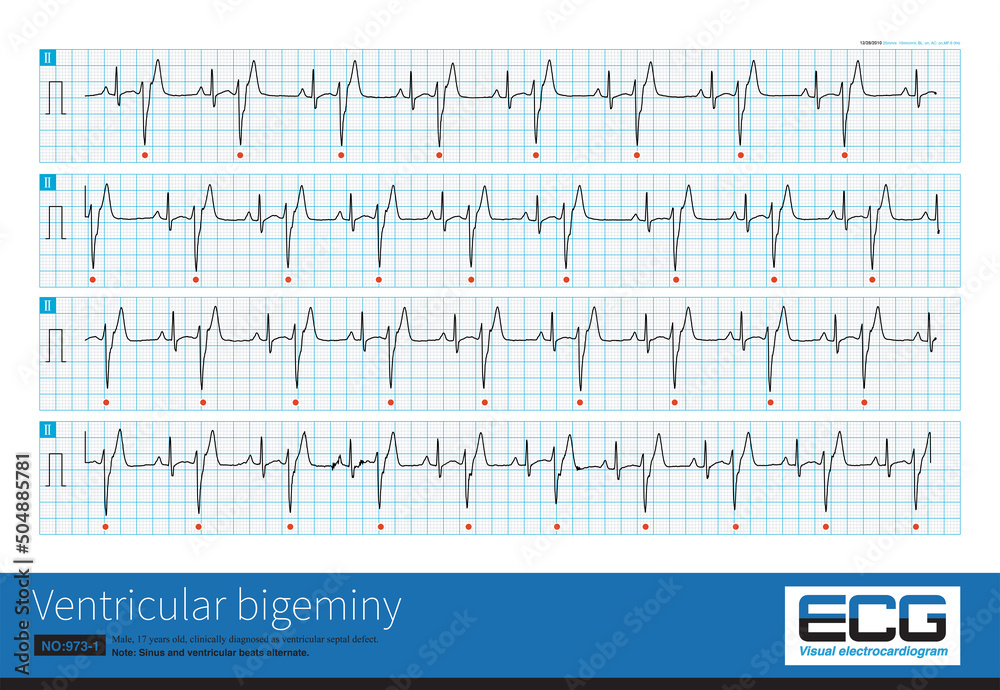
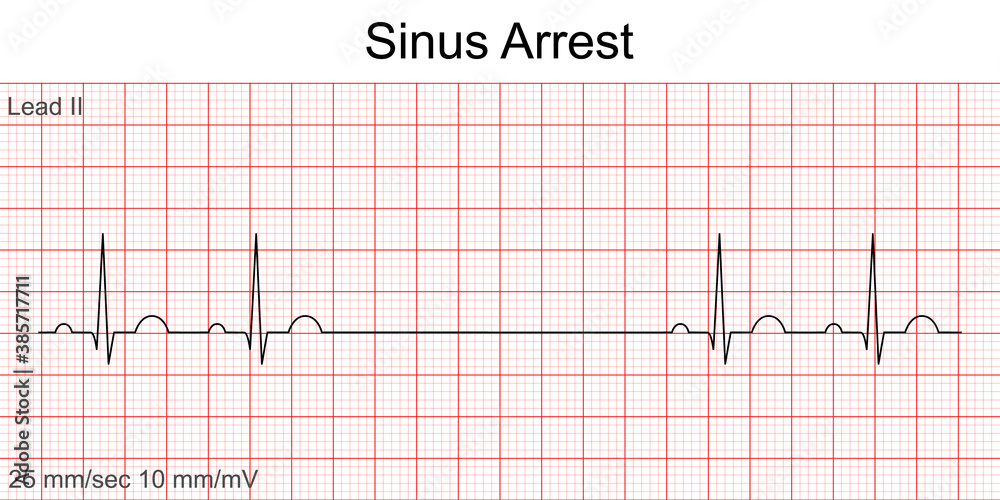
Vetor de Electrocardiogram show Sinus arrest pattern. Cardiac
The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). There are four primary alterations in the. Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial.
ECG Interpretation in Cardiac Arrest ECG Cases Emergency Medicine Cases
Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: There are four primary alterations in the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial.
ECG Interpretation in Cardiac Arrest ECG Cases Emergency Medicine Cases
The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). There are four primary alterations in the. During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of.
ECG Interpretation in Cardiac Arrest ECG Cases Emergency Medicine Cases
During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). There are four primary alterations in the. Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of.
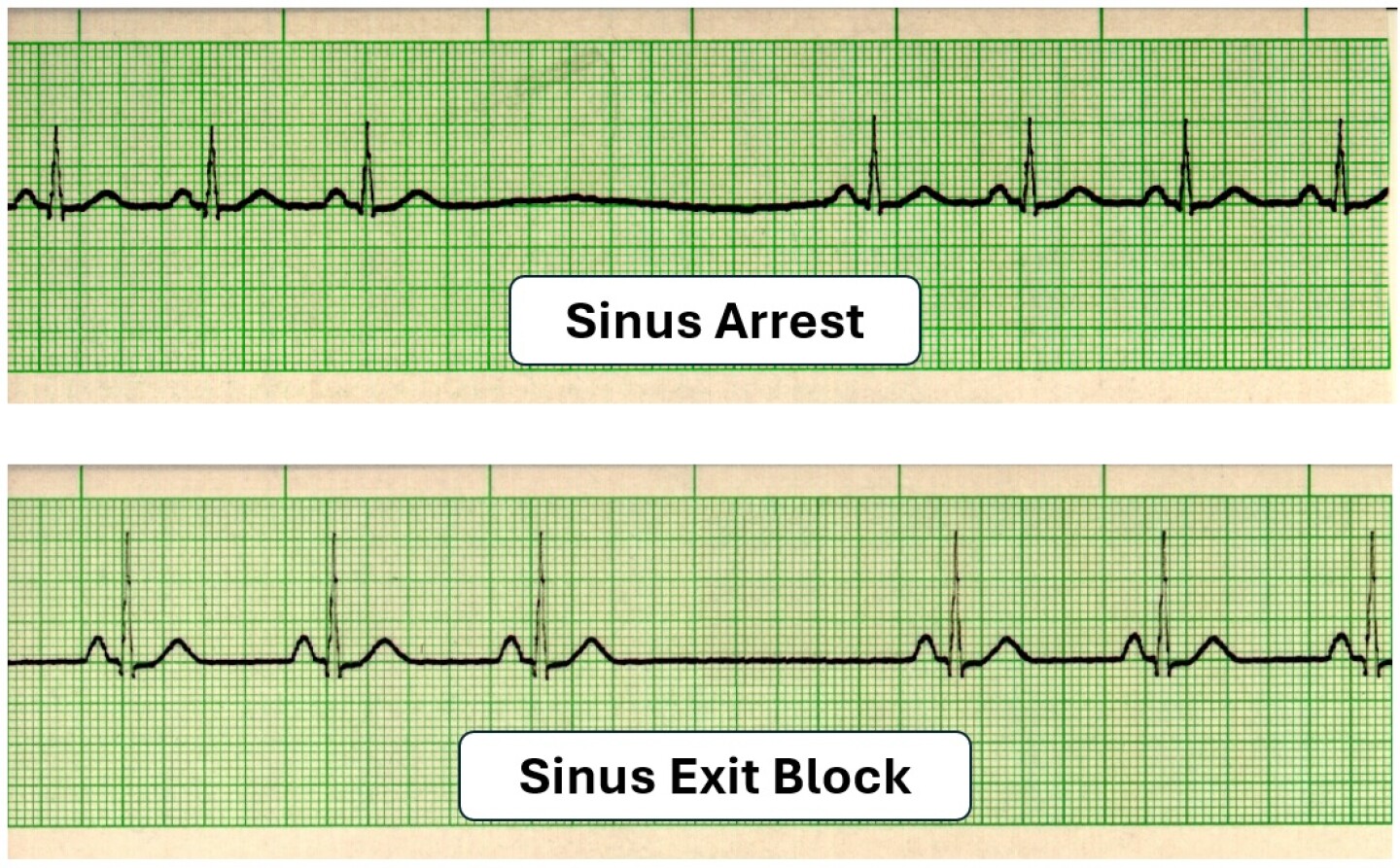
EKG Detective Sinus arrest vs. sinus exit block
There are four primary alterations in the. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: During cardiac arrest, recognition of ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (vf/vt) as shockable rhythms is crucial to the. Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of.
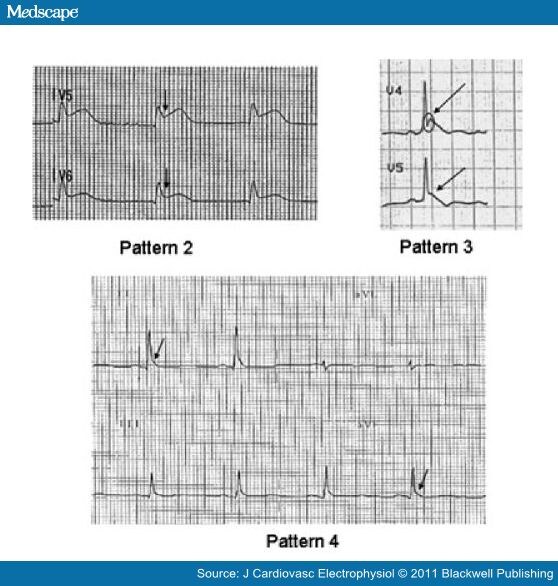
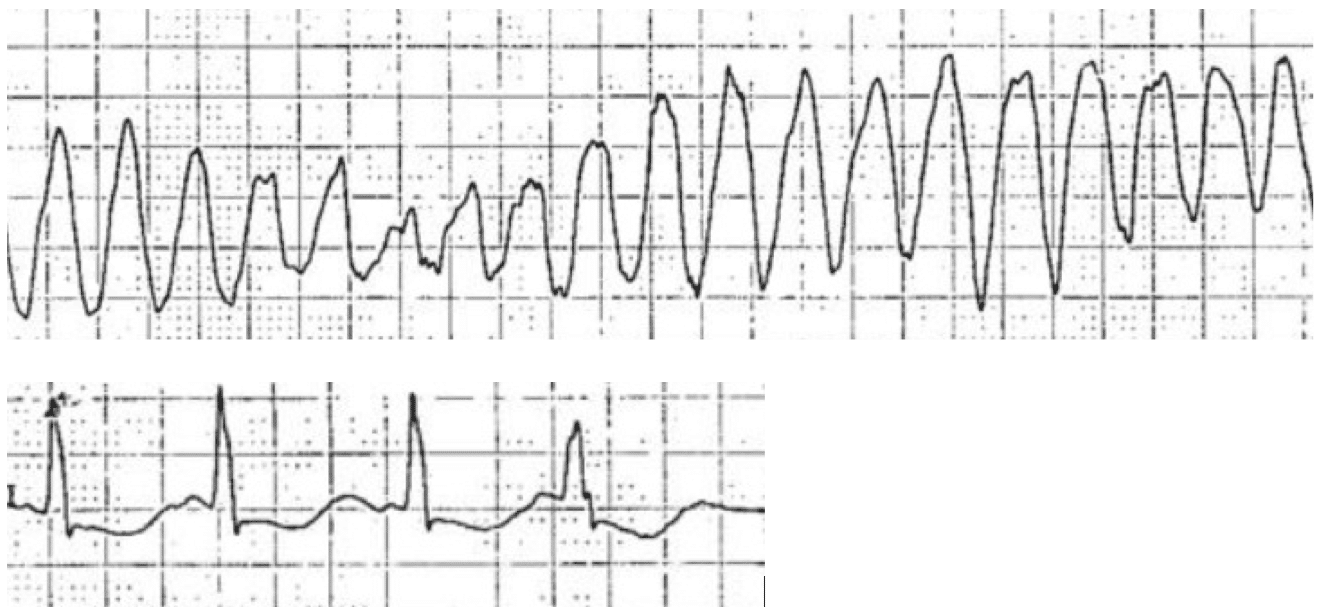
During Cardiac Arrest, Recognition Of Ventricular Fibrillation/Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (Vf/Vt) As Shockable Rhythms Is Crucial To The.
Cardiac arrest is a serious malfunction or stop of the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. The three phases following a sudden cardiac arrest were described by weisfeldt and becker (2002). Pulseless electrical activity in cardiac arrest: There are four primary alterations in the.